Organophosphate Poisoning Ppt
Management of organophosphate poisoning 1. Check airway, breathing, circulation. Monitor arterial oxygen saturation, cardiac rhythms, BP, Pulse rate. Look for signs. Describes OP poisoning, signs and symptoms, management and history.- authorSTREAM Presentation. Organophosphate poisoning: diagnosis and treatment. Organophosphate compounds are used as commercial insecticides. Organophosphate mechanism of toxicity.
[] Organophosphate poisoning is due to (OPs). Organophosphates are used as, medications, and. Symptoms include increased saliva and tear production,, vomiting,, sweating, muscle tremors, and confusion. Android Phone Drivers For Windows 7. While onset of symptoms is often within minutes to hours, some symptoms can take weeks to appear. Symptoms can last for days to weeks.
Organophosphate poisoning occurs most commonly as a attempt in farming areas of the and less commonly by accident. Exposure can be from drinking, breathing in the vapors, or skin exposure. The underlying mechanism involves the inhibition of (AChE), leading to the buildup of (ACh) in the body. Diagnosis is typically based on the symptoms and can be confirmed by measuring activity in the blood. Can present similarly.

Prevention includes banning very toxic types of organophosphates. Among those who work with pesticides the use of protective clothing and showering before going home is also useful. In those who have organophosphate poisoning the primary treatments are, such as, and. General measures such as and are also recommended. Attempts to decontaminate the stomach, with or other means, has not been shown to be useful. While there is a theoretical risk of health care workers taking care of a poisoned person becoming poisoned themselves, the degree of risk appears to be very small.
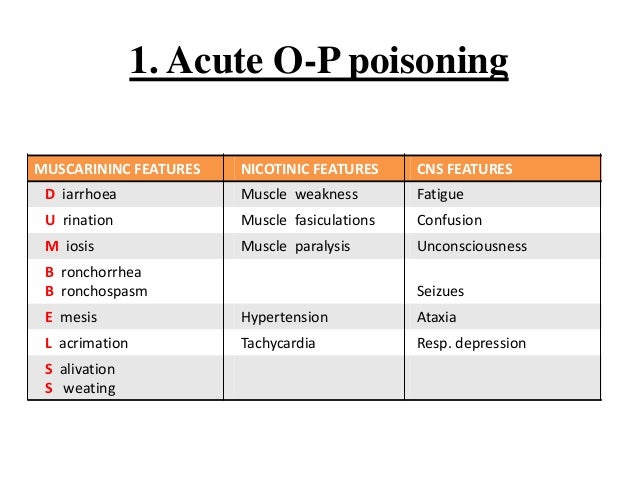
OPs are one of the most common causes of poisoning worldwide. There are nearly 3 million poisonings per year resulting in two hundred thousand deaths. Around 15% of people who are poisoned die as a result. Organophosphate poisoning has been reported at least since 1962. Contents • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Signs and symptoms [ ] The symptoms of organophosphate poisoning include muscle weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps, fasciculation, and paralysis. Other symptoms include hypertension, and hypoglycemia.
Overstimulation of in the central nervous system, due to accumulation of ACh, results in anxiety, headache, convulsions, ataxia, depression of respiration and circulation, tremor, general weakness, and potentially coma. When there is expression of muscarinic overstimulation due to excess acetylcholine at symptoms of visual disturbances, tightness in chest, wheezing due to bronchoconstriction, increased bronchial secretions, increased salivation, lacrimation, sweating, peristalsis, and urination can occur. The effects of organophosphate poisoning on muscarinic receptors are recalled using the (,,,,,, ) An additional mnemonic is MUDDLES: miosis, urination, diarrhea, diaphoresis, lacrimation, excitation, and salivation. The onset and severity of symptoms, whether acute or chronic, depends upon the specific chemical, the route of exposure (skin, lungs, or GI tract), the dose, and the individuals ability to degrade the compound, which the PON1 enzyme level will affect. Reproductive effects [ ] Certain reproductive effects in fertility, growth, and development for males and females have been linked specifically to OP pesticide exposure. Most of the research on reproductive effects has been conducted on farmers working with pesticides and insecticdes in rural areas.
For those males exposed to OP pesticides, poor semen and sperm quality have been seen, including reduced seminal volume and percentage motility, as well as a decrease in sperm count per ejacuate. In females menstrual cycle disturbances, longer pregnancies, spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, and some developmental effects in offspring have been linked to OP pesticide exposure. Prenatal exposure has been linked to impaired fetal growth and development. The effects of OP exposure on infants and children are at this time currently being researched to come to a conclusive finding. Evidence of OP exposure in pregnant mothers are linked to several health effects in the fetus. Some of these effects include delayed mental development, (PDD), morphological abnormalities in the cerebral surface.